Background
With the rapid advancement of emerging technologies such as 5G, IoT, and cloud computing, traditional metropolitan area network (MAN) architectures can no longer support large-scale, multi-service convergence. The next-generation MAN must not only support legacy foundational services but also integrate government and enterprise private networks, wireless, Internet of Vehicles, IoT, and more. It must also be self-protecting, efficient, and reliable. By introducing advanced technologies and architectures, the new MAN is designed to meet current service needs while also providing powerful support for future 5G-driven services.
Solution Overview
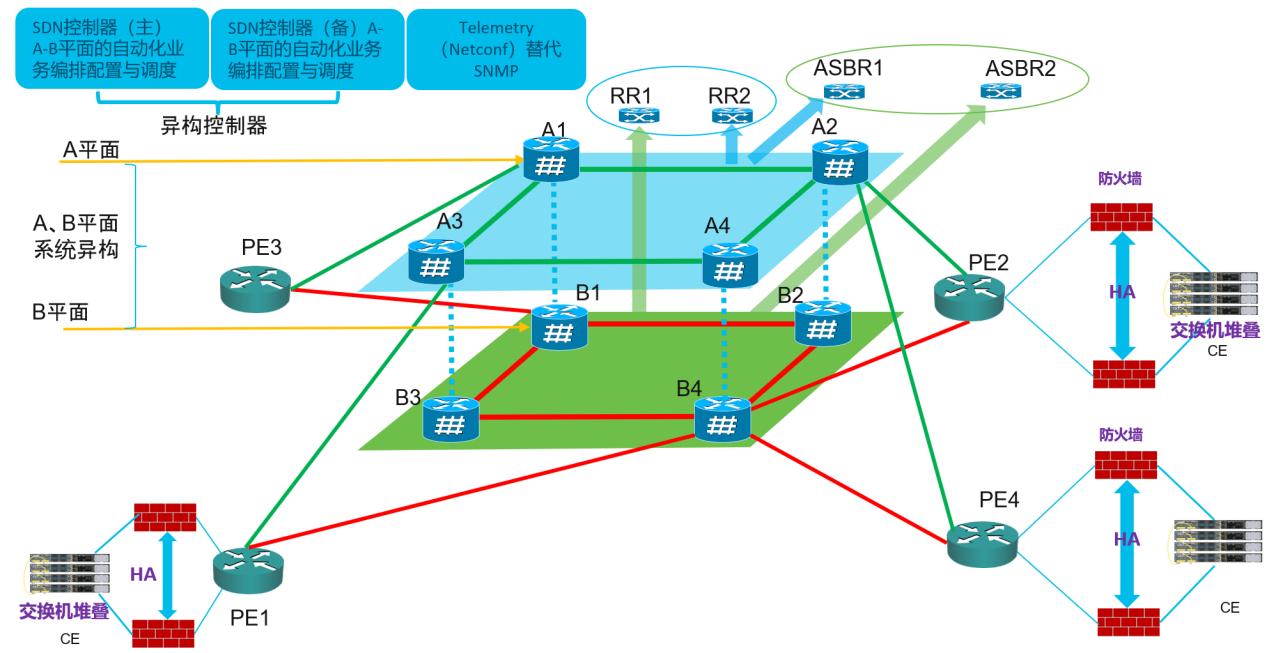
Dual-Plane Core Architecture
The core of the next-generation MAN adopts a dual-plane core design to ensure 100% safety and reliability. Various government and enterprise service PE (Provider Edge) nodes are dual-homed to both core layers, supporting integrated transmission for mobile 5G private networks and more.
- Dual-Plane Design: Plane A and Plane B use core routers from different vendors to ensure heterogeneity and high reliability. PE nodes are connected to both planes, ensuring uninterrupted services even if one plane fails.
- Segment Routing (SR) Technology: SR simplifies network protocols through source routing, enhancing traffic steering flexibility. SR's fast protection mechanism enables fault switchover within 50 ms, ensuring service continuity.
- Case Study: In a pilot project by a telecom operator, the dual-plane core architecture achieved 99.999% network reliability, reducing service downtime from minutes to milliseconds (seamless switchover).
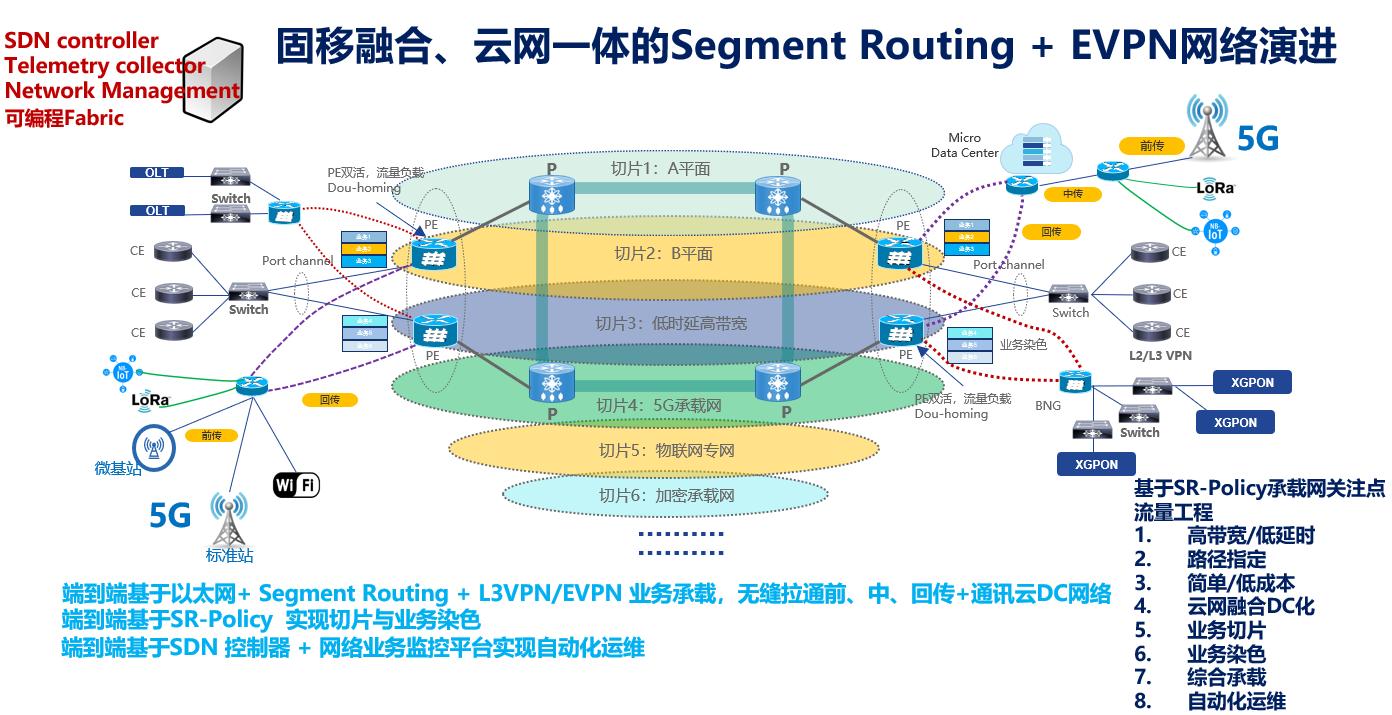
Aggregation and Access Layer Design
- Integrated Service Routers: High-performance, high-density compact routers supporting 10G–400G to meet future high-bandwidth service demands.
- SDN Controller: Automates business provisioning and enables refined visualized O&M using Telemetry and YANG models, greatly reducing manual work.
- Case Study: In a MAN upgrade project in a certain city, automated configuration at the aggregation/access layer reduced service provisioning time from hours to minutes, improving O&M efficiency by 70%.
Key Features
- One-Click Provisioning for Enterprise Leased Lines: Through centralized deployment in local data centers, traditional distributed deployment is replaced by a unified, service-oriented architecture. Provisioning time is reduced from 2–3 hours to seconds. Users can adjust bandwidth on demand via a self-service portal.
- Enterprise Smart Gateway Services: Provides government and enterprise customers with flexible self-organizing networks, branch interconnection, and seamless cloud integration. Visualization, applications, and big data analytics enable on-demand traffic scheduling and granular control.
Customer Pain Points & Challenges
- Complex Protocol Interoperability: Legacy products from different vendors lack SDN standards and compatibility. Traditional architectures require manual configuration of OSPF/ISIS/MPLS VPN, which is complex and time-consuming.
- O&M Complexity: Traditional architectures cannot meet automation demands. As network scale increases, manual O&M becomes costly and risky. For example, configuring and maintaining MPLS-TE is resource-intensive.
- Poor Scalability: Linearly scaled networks cannot quickly adapt to changing service requirements.
Customer Benefits
The new MAN architecture—with dual-plane core, integrated aggregation/access design, and SDN controller—resolves many of the limitations of traditional architectures. It enables high-efficiency multi-service transport and automated operations. As technologies like SR and EVPN become more widely adopted, MANs will evolve further toward intelligent and automated designs, offering robust support for 5G, IoT, and other emerging applications.