Solution Background
With the rapid development of quantitative and high-frequency trading, a leading securities firm is facing increasingly stringent latency requirements. Differences of mere milliseconds—or even microseconds—can directly impact the execution of trading strategies and overall profitability. Traditional trading systems suffer from latency bottlenecks in areas such as order processing, network transmission, and data exchange, and require comprehensive low-latency optimization.
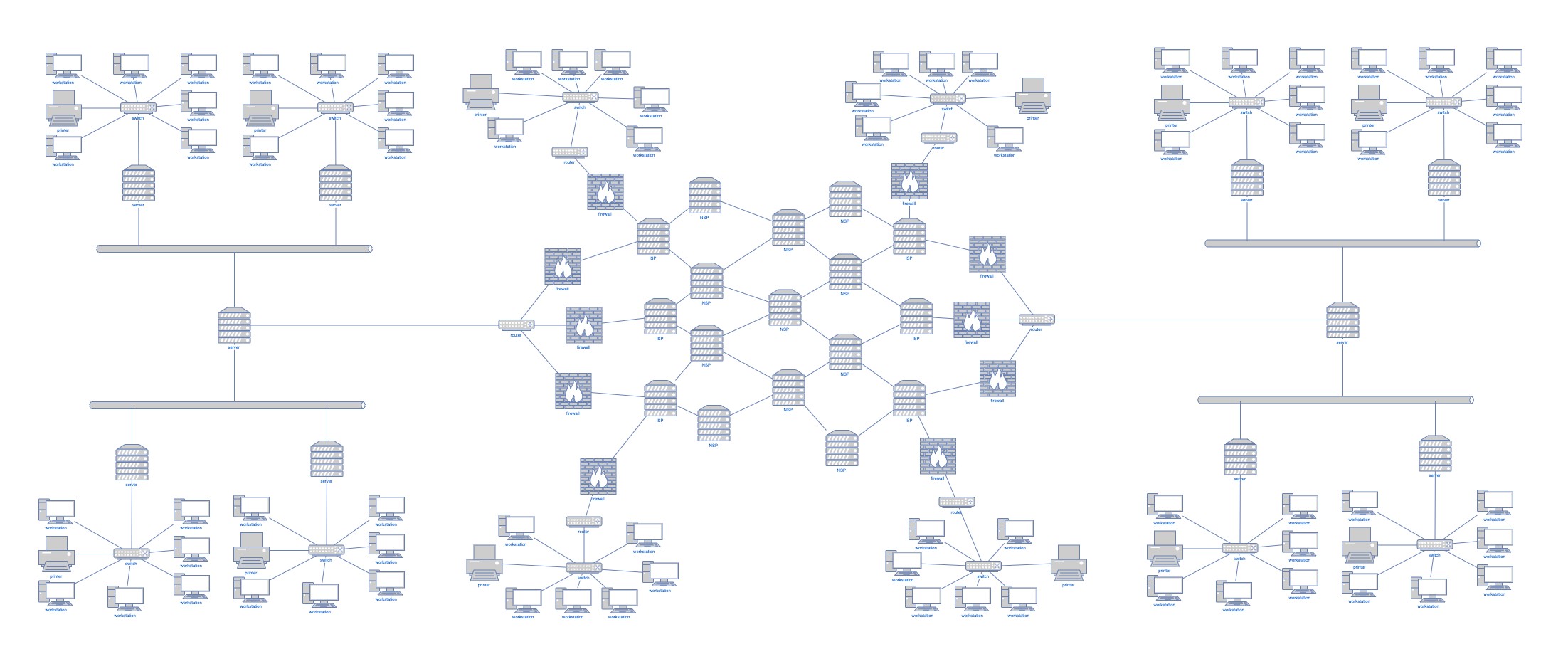
Solution Overview
This solution adopts a full-stack optimization strategy:
- Hardware Layer: Deploys FPGA accelerators and low-latency network interface cards (NICs)
- Network Architecture: Utilizes dedicated lines for direct exchange connectivity and ultra-simplified network topology
- Software Layer: Optimizes kernel parameters to enable zero-copy data transmission
- Intelligent Order Routing: Dynamically selects optimal transmission paths
- Time Synchronization: Implements nanosecond-level precision time synchronization to ensure full-link temporal control
Key Advantages
- End-to-end latency controlled within 50 microseconds
- Supports millions of orders per second
- Hardware acceleration improves performance by over 10×
- Smart routing algorithm dynamically optimizes data transmission paths
- Full-link visual monitoring enables real-time latency bottleneck identification
Customer Challenges
- Current system latency remains at the millisecond level, falling short of high-frequency trading (HFT) demands
- Unpredictable delays in market data transmission and order execution
- Poor scalability of the system, making it hard to handle trading volume surges
- Lack of effective tools for latency monitoring and analysis
- High hardware upgrade costs and uncertain ROI
Customer Benefits
- Gains competitive advantage by capturing more profit opportunities
- Increased order fill rate
- System throughput improved by several multiples
- Reduced slippage, resulting in higher annualized returns
- Built-in continuous optimization capabilities to meet future, more demanding latency requirements